给你一棵以 root 为根的二叉树和一个 head 为第一个节点的链表。
如果在二叉树中,存在一条一直向下的路径,且每个点的数值恰好一一对应以 head 为首的链表中每个节点的值,那么请你返回 True ,否则返回 False 。
一直向下的路径的意思是:从树中某个节点开始,一直连续向下的路径。
示例 1:
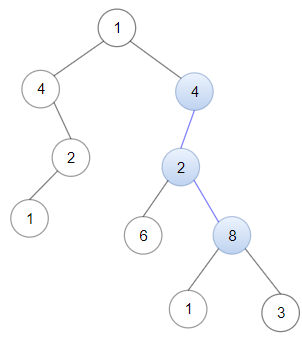
输入:head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] 输出:true 解释:树中蓝色的节点构成了与链表对应的子路径。
示例 2:
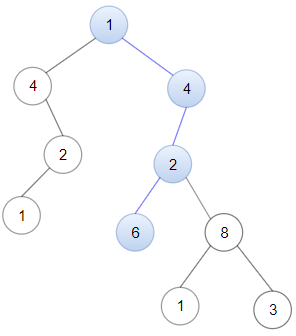


输入:head = [1,4,2,6], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] 输出:true
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,4,2,6,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] 输出:false 解释:二叉树中不存在一一对应链表的路径。
提示:
- 二叉树和链表中的每个节点的值都满足
1 <= node.val <= 100。 - 链表包含的节点数目在
1到100之间。 - 二叉树包含的节点数目在
1到2500之间。
**难度**: Medium
**标签**: 树、 链表、 动态规划、
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author : LG
"""
执行用时:108 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了96.06% 的用户
内存消耗:15.8 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了25.37% 的用户
解题思路:
先在树中找到与链表第一个节点相同值的 树节点
然后以这些树中节点为根的子树中寻找是否存在链表
"""
class Solution:
def isSubPath(self, head: ListNode, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def Sub(root, head): # 递归在子树中判断是否当前子树存在链表
# print(root, head)
if head==None: # 如果链表匹配完,则返回True,存在
return True
elif root and head:
if root.val == head.val:
if Sub(root.left, head.next):
return True
if Sub(root.right, head.next):
return True
nodes = []
def find(root, head): # 递归寻找树中所有与链表首节点值相同的树节点
if root:
if root.val == head.val: # 如果当前节点值等于链表首节点值,记录
nodes.append(root)
find(root.left, head)
find(root.right, head)
find(root, head)
for node in nodes:
if Sub(node, head): # 判断所有子树是否存在
return True
return False